Move Motion Controller
Move Hardware
- Model reference
- CECH-ZCM1U (bought in ?)
- CECH-ZCM1E (bought in europe)
- Main board reference
- YCON2_1.01 (dissassembled photos ---> http://www.ifixit.com/Teardown/PlayStation-Move-Teardown/3594/1)
- YCON2.5_1.03 (different Bluetooth chip, different 2-axis gyro "PR425A 2117 AEWEP")
- Note some components and testpoints (TP) are differet between models.
ARM STM32F103 VBT6 Y (32bit 72MHz MCU)
U19
http://www.st.com/mcu/devicedocs-STM32F103VB-110.html
| Reference | STM32 (Device family) | F (Procut type) | 103 (Device subfamily) | V (Pin count) | B (Flash memory size) | T (Package) | 6 (Temperature range) | Y (Options) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | STM32= ARM-based 32-bit microcontroller | F= general-purpose | 103= performance line | T= 36 pins C= 48 pins R= 64 pins V= 100 pins |
8= 64 Kbytes B= 128 Kbytes |
H= BGA T= LQFP U= VFQFPN |
6= -40 to +85 ºC 7= -40 to +105 ºC |
Unknown |
- Firmware
Calibration data for sensors (magnetometer, gyroscope, and acelerometer) is stored in the internal flash. This configuration is different for each country (mostly because the magnetometer/compass). When writing a flash dump made in a board for one region... to other board from other region this calibration values will be wrong
- Buses:
- 3x USART
- 2x SPI
- 2x I²C (magnetometer)
- 1x USB
- 1x CAN
- Pinout
| Pin # | Name | TP in YCON2_1.01 board | TP in YCON2.5_1.03 board | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 8 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 10 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| 12 | ||||
| 13 | ||||
| 14 | ||||
| 15 | ||||
| 16 | ||||
| 17 | ||||
| 18 | ||||
| 19 | ||||
| 20 | ||||
| 21 | ||||
| 22 | ||||
| 23 | ||||
| 24 | ||||
| 25 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 27 | ||||
| 28 | ||||
| 29 | ||||
| 30 | ||||
| 31 | ||||
| 32 | ||||
| 33 | ||||
| 34 | ||||
| 35 | ||||
| 36 | ||||
| 37 | ||||
| 38 | ||||
| 39 | ||||
| 40 | ||||
| 41 | ||||
| 42 | ||||
| 43 | ||||
| 44 | ||||
| 45 | ||||
| 46 | ||||
| 47 | ||||
| 48 | ||||
| 49 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 51 | ||||
| 52 | ||||
| 53 | ||||
| 54 | ||||
| 55 | ||||
| 56 | ||||
| 57 | ||||
| 58 | ||||
| 59 | ||||
| 60 | ||||
| 61 | ||||
| 62 | ||||
| 63 | ||||
| 64 | ||||
| 65 | ||||
| 66 | ||||
| 67 | ||||
| 68 | ||||
| 69 | ||||
| 70 | ||||
| 71 | ||||
| 72 | ||||
| 73 | ||||
| 74 | ||||
| 75 | ||||
| 76 | ||||
| 77 | ||||
| 78 | ||||
| 79 | ||||
| 80 | ||||
| 81 | ||||
| 82 | ||||
| 83 | ||||
| 84 | ||||
| 85 | ||||
| 86 | ||||
| 87 | ||||
| 88 | ||||
| 89 | ||||
| 90 | ||||
| 91 | ||||
| 92 | ||||
| 93 | ||||
| 94 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 96 | ||||
| 97 | ||||
| 98 | ||||
| 99 | ||||
| 100 |
STM LPR425AL (2-Axis Gyroscope)
The 2-axis gryoscope (likely an STM LPR425AL) is an analog sensor measuring rotation along the x- and y-axes
Is covered with a metal shield to avoid interferences (marked as 067S8 in some models), this makes his identification dificult
Y5250H 2029 K8QEZ (Z-Axis Gyroscope)
alt.no.: Y5250H 2005 4Y84AQ
alt.no.: Y5250H 2024 GPECQ
U14
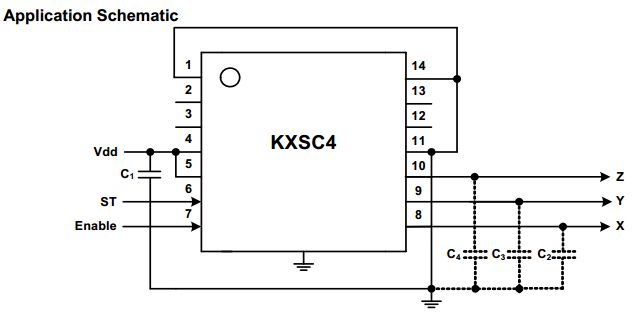
Kionix KXSC4 10227 2410 (3-Axis Accelerometer)
3-Axis Accelerometer
alt.no.: Kionix KXSC4-XLU 90831 3909
alt.no.: Kionix KXSC4 10115 2010
U12
Tri-Axis, 1.5g – 6g, Low Power Analog, 5x5x1.2mm DFN
The KXSC4 is a high-performance, low-power, analog output tri-axis accelerometer. This accelerometer is delivered in a 5 x 5 x 1.2 mm, 14-pin, DFN package with an operating temperature range of -40°C to +85°C.
The KXSC4 has a full-scale output range of ±2g and operates from a 1.8 V to 3.6 V DC supply (factory-programmable).
- Features:
- Factory-programmable, internal low-pass filter
- Low current consumption: 0.05 µA in standby, 230 µA at full power
- Factory-programmable ±1.5g to ±6g range
- Supply voltage range: 1.8 V to 3.6 V
- Analog output
- Embedded features
- Motion detection
- Orientation detection: report changes in face up, face down, +/- vertical and +/- horizontal orientation
- Self-test function
- RoHS compliant
http://www.kionix.com/accelerometers/kxsc4
http://www.kionix.com/sites/default/files/KXSC4%20Product%20Brief.pdf
http://www.kionix.com/sites/default/files/KXSC4-2050%20Specifications%20Rev%203.pdf
- Pinout
| Pin # | Name | Description | Move Board Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground. | |
| 2 | N.C | Not Connected Internally. | |
| 3 | N.C | Not Connected Internally. | |
| 4 | Vdd | Power supply input. Decouple this pin to ground with a 0.1uF ceramic capacitor (C1). | Decoupled with capacitor C42 |
| 5 | Reserved | Reserved (must be "Pulled-up to VDD" for normal operation). | Connected to pin 4 |
| 6 | ST | Self Test ("Pulled-down to GND" = normal operation. "Pulled-up to VDD" = self-test mode). | Connected to ? |
| 7 | Enable | Enable pin ("pulled-up to VDD" = normal operation. "Pulled-down to GND" = standby). | Connected to ? |
| 8 | X output | X-channel analog output (Optional filter capacitor, C2). | Connected to MCU pin# 24 (PA1). |
| 9 | Y output | Y-channel analog output (Optional filter capacitor, C3). | Connected to MCU pin# 18 (PC3). |
| 10 | Z output | Z-channel analog output (Optional filter capacitor, C4). | Connected to MCU pin# 26 (PA3). |
| 11 | GND | Ground. | |
| 12 | N.C | Not Connected Internally. | |
| 13 | N.C | Not Connected Internally. | |
| 14 | GND | Ground. |
- Output
1.6V is the zero output. The accelerometers have a scale of about +0.250V increment for each "g". Assuming that the chip is able to go full scale from 0V to 3V, this gives an absolute output of +-6g (this range is a configuration programmable at factory)
AKM AK8974 (3-Axis Magnetic Compass)
alt.no.:AKM8974 948D
alt.no.:AKM8974 008F
U13
http://www.chipworks.com/seamark.aspx?sm=s4%3BDatedfl11%3BDevCategory12%3BMEMS+Devicesm12%3BReleaseMonthm10%3BDeviceTypefl10%3BReportCode12%3BEXR-0908-802&cw=detail2
- Pinout
| Pin # | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 | ||
| 15 | ||
| 16 |
Cambridge Silicon Radio BC4RE A16U (Bluetooth transmitter)
U8?
http://www.csr.com/products/technology/bluetooth
- Pinout
| Pin # | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 | ||
| 15 | ||
| 16 | ||
| 17 | ||
| 18 | ||
| 19 | ||
| 20 | ||
| 21 | ||
| 22 | ||
| 23 | ||
| 24 | ||
| 25 | ||
| 26 | ||
| 27 | ||
| 28 | ||
| 29 | ||
| 30 | ||
| 31 | ||
| 32 | ||
| 33 | ||
| 34 | ||
| 35 | ||
| 36 | ||
| 37 | ||
| 38 | ||
| 39 | ||
| 40 |
ALPS 503A 04C (Radio Module)
LED2 (High Power RGB LED)
6 pins surface mounted RGB 2^24
- Soldered to the board with a ribbon cable (no connectors) with 4 lines marked as:
- LED_B
- LED_G
- LED_R
- LED_4R5 (VDD line)
TPS63030 (High Efficient Single Inductor Buck-Boost Converter)
alt.no.:CEE TI J 04P0
U6
Texas Instruments BQ24080 (1-cell Li-Ion Charger)
alt.no.:BRO 01J PDH2
alt.no.:BRO 04K 0948
U1
Li-Ion (Battery Pack)
4-168-108-01 / LIS1441
3.7V 1380 mAh
(typ 1520mAh)
Charge Current: 1.4A
Charge Voltage: 4.25V
External Conectors
USB connector
USB (Mini-B type) standard connector 5 pins
http://pinoutsguide.com/Slots/USB_pinout.shtml
Charging Station Pads
2 copper pads that are part of a little PCB with no traces that works as a support for the pads. Are soldered (no connectors) to the main board with 2 wires: black (ground) red (volts)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TkPFKrlWWwk
- This pads are common and has the same size and position than the Move Navigation Controller
Extension Connector
Marked in the plastic as "ext" and refered as "extension connector" in the Move Sharp Shooter "Instruction Manual.pdf"
8 pins custom made (exact alternative part not found yet)
This connector is used to communicate with the Move Sharp Shooter gun. The buttons, trigger, etc... of this gun can send signals to the move controller
| EXT connector pin number (from left to right) |
Connected to main board | MCU default firmware function | sony firmware function (pinout remapped ?) |
MoveCopter firmware function (pinout remapped) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.2v | |||
| 2 | 3.2v | |||
| 3 | MCU pin 41 (PE10) | TIM1_CH2N | No | |
| 4 | MCU pin 42 (PE11) | TIM1_CH2 | PPM output (input for the PC telemetry app) | |
| 5 | MCU pin 92 (PB6) | I2C1_SCL | USART1 TX (serial transmitter). Added to the project after D-lite manual | |
| 6 | MCU pin 93 (PB7) | I2C1_SDA | USART1 RX (serial receiver). Added to the project after D-lite manual | |
| 7 | GND | |||
| 8 | GND | |||
- Notes
- All the squematics and pinouts in "D-lite MoveCopter manual" and "Kenn Sebesta blog" related with this connector are taken directly from the main board (not from the external connector). The squematics explained in these pages are from an old model with different number of pins (some of them duplicated or displaced). There are at least 3 different board models where this pins are different, but in all models the lines are reordered at the "EXT connector" (and reduced to 8), all models has the same pinout externally explained here in ps3devwiki
- In MoveCopter bootloader several pins of MCU has been remaped, included 3 pins of "EXT connector" (for input/output data), and the 3 RGB lines from the LED + 1 line from the rumble motor (to controll 4 servo motors for the helices of the quadcopter)
Obsolete not-acurate notes The connector is soldered in a "children board" identifyed as "connector board", is connected with the "main board" with a 12 traces ribbon cable (and 2 pressure connectors). Only 4 lines of the ribbon cable are used for data signals (protected with a resistor and a diode in the children board) + 1 line for "ground" and 1 line for 3.2volts I will upload a complete squematic of this sub-circuit later
Software Related Projects
PSL1GHT
- https://github.com/ps3dev/PSL1GHT/tree/master/samples/input/gemsample
- https://github.com/ps3dev/PSL1GHT/tree/master/samples/input/gemtest
The PS Move API
Is a library to access the Sony Move Motion Controller via Bluetooth and USB directly from your PC (Linux, Mac OS X, Windows) without the need for a PS3. Mobile platforms are also supported (or planned): Support for MeeGo 1.2 Harmattan is already working, support for Android is in the works. The library is free software, released under a Simplified BSD License, so you can use it in both open source and proprietary closed-source applications, as long as you follow the license terms.
Git repository: https://github.com/thp/psmoveapi
Move On PC
PS Move Motion Controller as input device on PCs and mobile devices May 2012: We are participating in the Google Summer of Code. We will keep you updated about our progress here. The old code base will be archived in the Downloads section soon, and we will base our future MoveOnPC work on Thomas Perl's "PS Move API" project, but add support for tracking and computer vision to the library.
Blog: http://moveonpc.blogspot.com.es/
http://code.google.com/p/moveonpc/
Move Framework for Windows
With the Move Framework, you can integrate all the possibilities of motion tracking in your programs and games!. There are SDK's for C++ and C# developers. The project is no longer maintained
http://code.google.com/p/moveframework/ (src available with svn)
Motion In Joy for Windows
MotioninJoy is a driver, designed by a developer unconnected with Sony, intended to use all the features of the Sixaxis and Dualshock 3 controllers on a PC running Windows.
http://www.motioninjoy.com/wiki/help
http://forums.motioninjoy.com/viewtopic.php?f=33&t=929
Hardware Related Projects
Kenn Sebesta blog (PS3 Move hacking)
http://www.eissq.com/ps3_move/
D-Lite MoveCopter
"CopterControl bootloader" port for "Move controller"
Is a custom bootloader/firmware for the ARM STM32 microcontroller series. The installation is composed by the "bootloader" (move hardware specific, installed by JTAG) and the "flight firmware" (common for all STM32 microcontrollers, installed by USB)
The flight firmware is intended to stabilish a flying quadcopter using data from position sensors (like the gyroscopes and the 3-axis acelerometers in move)
http://wiki.openpilot.org/display/Doc/D-Lite%27s+PS3+MoveCopter
http://forums.openpilot.org/topic/5526-coptercontrol-on-a-game-controller/
http://forums.openpilot.org/topic/5526-coptercontrol-on-a-game-controller/page__st__40#entry24579
http://forums.openpilot.org/topic/5526-coptercontrol-on-a-game-controller/page__st__140#entry80016
http://git.openpilot.org/changelog/~br=D-Lite%402fMoveCopter_MARG/OpenPilot
http://wiki.openpilot.org/display/CC/CopterControl+Home
http://wiki.openpilot.org/display/Doc/Ground+Control+Station+User+Manual
http://www.openpilot.org/products/openpilot-coptercontrol-platform/
http://forums.openpilot.org/topic/5526-coptercontrol-on-a-game-controller/page__st__140#entry81223