GbLAN: Difference between revisions
m (→pinout) |
|||
| Line 399: | Line 399: | ||
{| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" border="#999" class="wikitable" style="border:1px solid #999; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" border="#999" class="wikitable" style="border:1px solid #999; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
|- bgcolor="#cccccc" | |- bgcolor="#cccccc" | ||
! Pin # !! Name !! | ! Pin # !! Name !! Pin Type !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 || | | 1 || CONFIG[1] || I || Hardware Configuration | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2 || | | 2 || CONFIG[2] || I || Hardware Configuration | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || | | 3 || CONFIG[3] || I || Hardware Configuration | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || | | 4 || CLK125 || O || 125 MHz Clock Output. When Hardware reset is asserted, a 25 MHz clock is generated output, otherwise a 125 MHz clock is output. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 5 || | | 5 || DVDD || Power || Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 6 || | | 6 || LED[0] || O || LED/Interrupt outputs | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 7 || | | 7 || VDDO || Power || 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V non-RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDO must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDO. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 8 || | | 8 || LED[1] || O || LED/Interrupt outputs | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 9 || | | 9 || LED[2] || O || LED/Interrupt outputs | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 10 || | | 10 || RESETn || I || Hardware reset. Active low. 0 = Reset 1 = Normal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 11 || | | 11 || TRSTn || I, PU || Boundary scan test reset input. Active low. TRSTn contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor as per the 1149.1 specification. After power up, the JTAG state machine should be reset by applying a low signal on this pin, or by keeping TMS high and applying 5 TCK pulses, or by pulling this pin low by a 4.7 kohm resistor. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 12 || | | 12 || DIS_REG12 || I || 1.2V Regulator Disable. Tie to VDDO to disable, tie to VSS to enable. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 13 || | | 13 || DVDD || Power || Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 14 || | | 14 || AVDDR || || 1.2V Regulator supply - 1.8V AVDDR can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. If the | ||
1.2V regulator is not used, AVDDR must still be tied to 1.8V. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 15 || | | 15 || AVDDR || || 1.2V Regulator supply - 1.8V AVDDR can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. If the | ||
1.2V regulator is not used, AVDDR must still be tied to 1.8V. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 16 || | | 16 || AVDDX || Power || 1.8V Regulator supply - 2.5V, 3.3V, (or 1.8V). AVDDX must be supplied externally. Note that this supply must be the same voltage as AVDDC. If the 1.8V regulator is not used, then it means a 1.8V supply is in the system. AVDDX (along with AVDDC) would be tied to 1.8V in this case. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 17 || | | 17 || CTRL18 || O || 1.8V Regulator Control. This signal ties to the base of the BJT. If the 1.8V regulator is not used it can be left floating. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 18 || | | 18 || NC || NC || No connect. These pins are not connected to the die so they can be connected to anything on the board. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 19 || | | 19 || MDIN[3] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[3] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 20 || | | 20 || MDIP[3] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[3] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 21 || | | 21 || AVDD || Power || Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 22 || | | 22 || AVDD || Power || Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 23 || | | 23 || MDIN[2] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[2] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 24 || | | 24 || MDIP[2] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[2] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 25 || | | 25 || MDIN[1] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[1] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 26 || | | 26 || MDIP[1] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[1] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 27 || | | 27 || AVDD || Power || Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 28 || | | 28 || NC || NC || No connect. These pins are not connected to the die so they can be connected to anything on the board. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 29 || | | 29 || AVDD || Power || Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 30 || | | 30 || MDIN[0] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[0] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 31 || | | 31 || MDIP[0] || I/O, D || Media Dependent Interface[0] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 32 || | | 32 || TSTPT || O || Test Point | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 33 || | | 33 || RSET || I || Constant voltage reference. External 4.99 kohm 1% resistor connection to VSS required for each pin. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 34 || | | 34 || AVDDC || || Analog supply - 1.8V or 2.5V, or 3.3V. AVDDC must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power AVDDC. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 35 || | | 35 || HSDACN || O || AC Test Point. Connect the AC testpoints with a 50 ohm termination resistor to VSS for IEEE testing and | ||
debug purposes. If debug and IEEE testing are not of importance, these pins can be left floating. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 36 || | | 36 || HSDACP || O || AC Test Point. Connect the testpoints with a 50 ohm termination resistor to VSS for IEEE testing and | ||
debug purposes. If debug and IEEE testing are not of importance, these pins can be left floating. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 37 || | | 37 || AVDDC || || Analog supply - 1.8V or 2.5V, or 3.3V. AVDDC must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power AVDDC. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 38 || | | 38 || XTAL_IN || I || Reference Clock. 25 MHz ± 50 ppm tolerance crystal reference or oscillator input. | ||
NOTE: If AVDDC is tied to 1.8V, then the XTAL_IN pin is not 2.5V/3.3V tolerant. | |||
If AVDDC is tied to 2.5V, then the XTAL_IN pin is not 3.3V tolerant. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 39 || | | 39 || XTAL_OUT || O || Reference Clock. 25 MHz ± 50 ppm tolerance crystal reference. When the | ||
XTAL_OUT pin is not connected, it should be left floating. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 40 || | | 40 || DVDD || Power || Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 41 || | | 41 || TMS || I, PU || Boundary scan test mode select input. TMS contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 42 || | | 42 || TCK || I, PU || Boundary scan test clock input. TCK contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 43 || | | 43 || TDI || I || Boundary scan test data input | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 44 || | | 44 || TDO || O || Boundary scan test data output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 45 || | | 45 || MDIO || I/O || MDIO is the management data. MDIO transfers management data in and out of the device synchronously to MDC. This pin requires a pull-up resistor in a range from 1.5 kohm to 10 kohm. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 46 || | | 46 || VDDO || Power || 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V non-RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDO must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDO. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 47 || | | 47 || DVDD || Power || Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 48 || | | 48 || MDC || I || MDC is the management data clock reference for the serial management interface. A continuous clock stream is not expected. The maximum frequency supported is 8.3 MHz. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 49 || | | 49 || RX_CTRL || O || RGMII Receive Control. RX_DV is presented on the rising edge of RX_CLK. A logical derivative of RX_DV and RX_ER is presented on the falling edge of RX_CLK. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 50 || | | 50 || RXD[0] || O || RGMII Receive Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 51 || | | 51 || RXD[1] || O || RGMII Receive Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 52 || | | 52 || VDDOR || Power || 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDOR must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDOR. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 53 || | | 53 || RX_CLK || O || RGMII Receive Clock provides a 125 MHz, 25 MHz, or 2.5 MHz reference clock with ± 50 ppm tolerance derived from the received data stream depending on speed. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 54 || | | 54 || RXD[2] || O || RGMII Receive Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 55 || | | 55 || RXD[3] || O || RGMII Receive Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 56 || | | 56 || VDDOR || Power || 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDOR must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDOR. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 57 || | | 57 || VREF || I || RGMII input voltage reference. Must be set to VDDOR/2 when used as 1.8V HSTL, 2.5V SSTL_2, and 3.3V. Set to VDDOR when used as 2.5V LV CMOS. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 58 || | | 58 || TXD[0] || I || RGMII Transmit Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 59 || | | 59 || TXD[1] || I || RGMII Transmit Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 60 || | | 60 || TCX_CLK || I || RGMII Transmit Clock provides a 125 MHz, 25 MHz, or 2.5 MHz reference clock with ± 50 ppm tolerance depending on speed. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 61 || | | 61 || TXD[2] || I || RGMII Transmit Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 62 || | | 62 || TXD[3] || I || RGMII Transmit Data | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 63 || | | 63 || TX_CTRL || I || RGMII Transmit Control. TX_EN is presented on the rising edge of TX_CLK. A logical derivative of TX_EN and TX_ER is presented on the falling edge of TX_CLK. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 64 || - || || - | | 64 || CONFIG[0] || I || Hardware Configuration | ||
|- | |||
| EPAD || VSS || GND || Ground to device. The 64-pin QFN package has an exposed die pad (E-PAD) at its base. This E-PAD must be soldered to VSS. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 18 July 2011
Gigabit LAN
The PS3 has 1 Gigabit Ethernet port. The port accepts Auto-MDIX (automatic medium-dependent interface crossover), so no need for special crosscables when hooking up the PS3 direct to the PC.
Gigabit LAN chips used
A sample of the GbLAN chips in different PS3 models:
| Ports | Size | Speed | Voltage | Packaging | Manufacturer | Serial Number | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 (3 used) | 20x20mm | Xtal X3501: 25MHz | 3.3V/1.9V/1.2V | 144-pin TQFP | Marvell | 88E6108-LAR1 | Used in earlier models |
| - | - | - | - | 64-pin QFN | Marvell | Alaska 88E1118R-NNC2 | Used in Slim models |
Marvell 88E6108-LAR1
Datasheet: (not available)
productcode meaning: 88E6108-LAR1 Type: Ethernet Speed : 1Gbps Ports : 8 Package : 144-TQFP (sorry, no explaination yet)
The Marvell 88E6108-LAR1 is sort of a switching hub chip, with several ports that can be used in different configurations:
Port 0 (usuable as MDI 4 dif.pair) : unused (tied to ground) Port 1 (usuable as MDI 4 dif.pair) : unused (tied to ground) Port 2 (usuable as MDI 4 dif.pair) : wired to external UTP connector Port 3 (GMII): Wired to SB Port 4 (usable as TX/RX dif.pair)(100FX): wired to Wifi Port 5 (usable as TX/RX dif.pair): unused (tied to ground) Port 6 (usable as TX/RX dif.pair): unused (tied to ground) Port 7 (usable as TX/RX dif.pair): unused (tied to ground)
Pinout IC3503
Productcode: 88E6108-B2-LAR1C000-P123 | PartNo.: 6-710-202-01
| Pin # | Name | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RST | Power / Led / Xtal etc | - |
| 2 | AVDD | - | |
| 3 | NC | No Connection | |
| 4 | NC | No Connection | |
| 5 | NC | No Connection | |
| 6 | AVDD | - | |
| 7 | XTAL_IN | - | |
| 8 | XTAL_OUT | - | |
| 9 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 10 | NC | No Connection | |
| 11 | NC | No Connection | |
| 12 | AVDD | - | |
| 13 | NC | No Connection | |
| 14 | NC | No Connection | |
| 15 | P0_LED3 | - | |
| 16 | P0_LED2 | - | |
| 17 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 18 | P0_LED1 | - | |
| 19 | P0_LED0 | - | |
| 20 | VDDO_LED | - | |
| 21 | P1_LED3 | - | |
| 22 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 23 | P1_LED3 | - | |
| 24 | P1_LED1 | - | |
| 25 | P1_LED0 | - | |
| 26 | VDDO_LED | - | |
| 27 | P2_LED3 | - | |
| 28 | P2_LED2 | - | |
| 29 | P2_LED1 | - | |
| 30 | P2_LED0 | - | |
| 31 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 32 | MDC_PHY/PPU_EN | - | |
| 33 | VDDO_SMI_PHY | - | |
| 34 | MDIO_PHY | - | |
| 35 | VDD_PLL | - | |
| 36 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 37 | P7_TXP | Port 7 (unused) |
- |
| 38 | P7_TXN | - | |
| 39 | P7_VDDAH | Ground | |
| 40 | P7_RXP | - | |
| 41 | P7_RXN | - | |
| 42 | VSS | Ground | |
| 43 | P6_RXP | Port 6 (unused) |
- |
| 44 | P6_RXN | - | |
| 45 | P6_VDDAH | Ground | |
| 46 | P6_TXN | - | |
| 47 | P6_TXP | - | |
| 48 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 49 | P5_TXP | Port 5 (unused) |
- |
| 50 | P5_TXN | - | |
| 51 | P5_VDDAH | Ground | |
| 52 | P5_RXP | - | |
| 53 | P5_RXN | - | |
| 54 | VSS | Ground | |
| 55 | P4_RXN | Port 4 (100FX) | - |
| 56 | P4_RXP | - | |
| 57 | P4_VDDAH | - | |
| 58 | P4_TXN | - | |
| 59 | P4_TXP | - | |
| 60 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 61 | VDD_P3 | Port 3 (GMII) | - |
| 62 | P3_CLK125N | - | |
| 63 | P3_TXEN/HALFDPX | - | |
| 64 | P3_TXD7/MODE2 | - | |
| 65 | P3_TXD6/MODE1 | - | |
| 66 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 67 | P3_TXD5/MODE0 | - | |
| 68 | P3_TXD4/ADDR4 | - | |
| 69 | VDD0_P3 | - | |
| 70 | P3_TXD3/ADDR3 | - | |
| 71 | P3_TXD2/ADDR2 | - | |
| 72 | P3_TXD1/ADDR1 | - | |
| 73 | P3_TXD0/ADDR0 | - | |
| 74 | P3_TXCLK | - | |
| 75 | P3_GTXCLK | - | |
| 76 | VDD0_P3 | - | |
| 77 | P3_RXDV | - | |
| 78 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 79 | P3_RXXEA | - | |
| 80 | P3_RXD7 | - | |
| 81 | P3_RXD6 | - | |
| 82 | P3_RXD5 | - | |
| 83 | P3_RXD4 | - | |
| 84 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 85 | P3_RXD3 | - | |
| 86 | VDDO_P3 | - | |
| 87 | P3_RXD2 | - | |
| 88 | P3_RXD1 | - | |
| 89 | P3_RXD0 | - | |
| 90 | P3_RXCLK | - | |
| 91 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 92 | P3_CRS | - | |
| 93 | P3_COL | - | |
| 94 | P3_ENABLE_PD | - | |
| 95 | INTn | - | |
| 96 | MDIO_CPU | - | |
| 97 | MDC_CPU | - | |
| 98 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 99 | EE_DOUT | - | |
| 100 | VDDO_SMI_CPU | - | |
| 101 | EE_DIN/HD_FLOW_DIS | - | |
| 102 | EE_CLK/FD_FLOW_DIS | - | |
| 103 | EE_CS/EE_1K | - | |
| 104 | VDD_CORE | - | |
| 105 | SW_MODE0 PU | - | |
| 106 | SW_MODE1 PU | - | |
| 107 | VSS | Ground | |
| 108 | RESETn | - | |
| 109 | VSS | Port 2 (MDI) | Ground |
| 110 | P2_MDIN3 | - | |
| 111 | P2_MDIP3 | - | |
| 112 | P2_AVDD | - | |
| 113 | P2_MDIN2 | - | |
| 114 | P2_MDIP2 | - | |
| 115 | P2_MDIN1 | - | |
| 116 | P2_MDIP1 | - | |
| 117 | P2_AVDD | - | |
| 118 | P2_AVDD | - | |
| 119 | P2_MDIN0 | - | |
| 120 | P2_MDIP0 | - | |
| 121 | VSS | Port 1 (MDI) | Ground |
| 122 | P1_MDIN3 | - | |
| 123 | P1_MDIP3 | - | |
| 124 | P1_AVDD | - | |
| 125 | P1_MDIN2 | - | |
| 126 | P1_MDIP2 | - | |
| 127 | P1_MDIN1 | - | |
| 128 | P1_MDIP1 | - | |
| 129 | P1_AVDD | - | |
| 130 | P1_AVDD | - | |
| 131 | P1_MDIN0 | - | |
| 132 | P1_MDIP0 | - | |
| 133 | VSS | Port 0 (MDI) | Ground |
| 134 | P0_MDIN3 | - | |
| 135 | P0_MDIP3 | - | |
| 136 | P0_AVDD | - | |
| 137 | P0_MDIN2 | - | |
| 138 | P0_MDIP2 | - | |
| 139 | P0_MDIN1 | - | |
| 140 | P0_MDIP1 | - | |
| 141 | P0_AVDD | - | |
| 142 | P0_AVDD | - | |
| 143 | P0_MDIN0 | - | |
| 144 | P1_MDIP0 | - |
Pinout CN3501
Connectortype: RJ45 modular jack with LED | PartNo.: 1-820-763-12
| Pin # | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | - |
| 2 | TP1+ | - |
| 3 | TP1- | - |
| 4 | TP2+ | - |
| 5 | TP2- | - |
| 6 | GND | - |
| 7 | TP3+ | - |
| 8 | TP3- | - |
| 9 | TP4+ | - |
| 10 | TP4- | - |
| 11 | VCC | - |
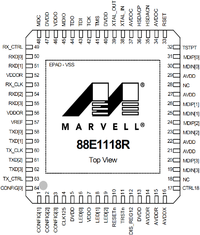
Marvell Alaska 88E1118R-NNC2
productcode meaning: 88E1118R-NNC2 = 10/100/1000BASE-T PHY with RGMII Type: Ethernet Speed : 1Gbps VCC: 1.8V (regulators can be supplied with 1.8V, 2.5V or 3.3V) I/O: 1.8V, 2.5V or 3.3V 125MHz Clock input Package : 64-pin QFN (sorry, no explaination yet)
pinout
(nothing here, please help fill this in)
| Pin # | Name | Pin Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CONFIG[1] | I | Hardware Configuration |
| 2 | CONFIG[2] | I | Hardware Configuration |
| 3 | CONFIG[3] | I | Hardware Configuration |
| 4 | CLK125 | O | 125 MHz Clock Output. When Hardware reset is asserted, a 25 MHz clock is generated output, otherwise a 125 MHz clock is output. |
| 5 | DVDD | Power | Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. |
| 6 | LED[0] | O | LED/Interrupt outputs |
| 7 | VDDO | Power | 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V non-RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDO must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDO. |
| 8 | LED[1] | O | LED/Interrupt outputs |
| 9 | LED[2] | O | LED/Interrupt outputs |
| 10 | RESETn | I | Hardware reset. Active low. 0 = Reset 1 = Normal |
| 11 | TRSTn | I, PU | Boundary scan test reset input. Active low. TRSTn contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor as per the 1149.1 specification. After power up, the JTAG state machine should be reset by applying a low signal on this pin, or by keeping TMS high and applying 5 TCK pulses, or by pulling this pin low by a 4.7 kohm resistor. |
| 12 | DIS_REG12 | I | 1.2V Regulator Disable. Tie to VDDO to disable, tie to VSS to enable. |
| 13 | DVDD | Power | Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. |
| 14 | AVDDR | 1.2V Regulator supply - 1.8V AVDDR can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. If the
1.2V regulator is not used, AVDDR must still be tied to 1.8V. | |
| 15 | AVDDR | 1.2V Regulator supply - 1.8V AVDDR can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. If the
1.2V regulator is not used, AVDDR must still be tied to 1.8V. | |
| 16 | AVDDX | Power | 1.8V Regulator supply - 2.5V, 3.3V, (or 1.8V). AVDDX must be supplied externally. Note that this supply must be the same voltage as AVDDC. If the 1.8V regulator is not used, then it means a 1.8V supply is in the system. AVDDX (along with AVDDC) would be tied to 1.8V in this case. |
| 17 | CTRL18 | O | 1.8V Regulator Control. This signal ties to the base of the BJT. If the 1.8V regulator is not used it can be left floating. |
| 18 | NC | NC | No connect. These pins are not connected to the die so they can be connected to anything on the board. |
| 19 | MDIN[3] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[3] |
| 20 | MDIP[3] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[3] |
| 21 | AVDD | Power | Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. |
| 22 | AVDD | Power | Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. |
| 23 | MDIN[2] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[2] |
| 24 | MDIP[2] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[2] |
| 25 | MDIN[1] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[1] |
| 26 | MDIP[1] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[1] |
| 27 | AVDD | Power | Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. |
| 28 | NC | NC | No connect. These pins are not connected to the die so they can be connected to anything on the board. |
| 29 | AVDD | Power | Analog supply. 1.8V. AVDD can be supplied externally with 1.8V, or via the 1.8V regulator. |
| 30 | MDIN[0] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[0] |
| 31 | MDIP[0] | I/O, D | Media Dependent Interface[0] |
| 32 | TSTPT | O | Test Point |
| 33 | RSET | I | Constant voltage reference. External 4.99 kohm 1% resistor connection to VSS required for each pin. |
| 34 | AVDDC | Analog supply - 1.8V or 2.5V, or 3.3V. AVDDC must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power AVDDC. | |
| 35 | HSDACN | O | AC Test Point. Connect the AC testpoints with a 50 ohm termination resistor to VSS for IEEE testing and
debug purposes. If debug and IEEE testing are not of importance, these pins can be left floating. |
| 36 | HSDACP | O | AC Test Point. Connect the testpoints with a 50 ohm termination resistor to VSS for IEEE testing and
debug purposes. If debug and IEEE testing are not of importance, these pins can be left floating. |
| 37 | AVDDC | Analog supply - 1.8V or 2.5V, or 3.3V. AVDDC must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power AVDDC. | |
| 38 | XTAL_IN | I | Reference Clock. 25 MHz ± 50 ppm tolerance crystal reference or oscillator input.
NOTE: If AVDDC is tied to 1.8V, then the XTAL_IN pin is not 2.5V/3.3V tolerant. If AVDDC is tied to 2.5V, then the XTAL_IN pin is not 3.3V tolerant. |
| 39 | XTAL_OUT | O | Reference Clock. 25 MHz ± 50 ppm tolerance crystal reference. When the
XTAL_OUT pin is not connected, it should be left floating. |
| 40 | DVDD | Power | Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. |
| 41 | TMS | I, PU | Boundary scan test mode select input. TMS contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor. |
| 42 | TCK | I, PU | Boundary scan test clock input. TCK contains an internal 150 kohm pull-up resistor. |
| 43 | TDI | I | Boundary scan test data input |
| 44 | TDO | O | Boundary scan test data output |
| 45 | MDIO | I/O | MDIO is the management data. MDIO transfers management data in and out of the device synchronously to MDC. This pin requires a pull-up resistor in a range from 1.5 kohm to 10 kohm. |
| 46 | VDDO | Power | 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V non-RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDO must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDO. |
| 47 | DVDD | Power | Digital core supply - 1.2V. DVDD can be supplied externally with 1.2, or via the 1.2V regulator. |
| 48 | MDC | I | MDC is the management data clock reference for the serial management interface. A continuous clock stream is not expected. The maximum frequency supported is 8.3 MHz. |
| 49 | RX_CTRL | O | RGMII Receive Control. RX_DV is presented on the rising edge of RX_CLK. A logical derivative of RX_DV and RX_ER is presented on the falling edge of RX_CLK. |
| 50 | RXD[0] | O | RGMII Receive Data |
| 51 | RXD[1] | O | RGMII Receive Data |
| 52 | VDDOR | Power | 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDOR must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDOR. |
| 53 | RX_CLK | O | RGMII Receive Clock provides a 125 MHz, 25 MHz, or 2.5 MHz reference clock with ± 50 ppm tolerance derived from the received data stream depending on speed. |
| 54 | RXD[2] | O | RGMII Receive Data |
| 55 | RXD[3] | O | RGMII Receive Data |
| 56 | VDDOR | Power | 1.8V, 2.5V, or 3.3V RGMII digital I/O supply. VDDOR must be supplied externally. Do not use the 1.8V regulator to power VDDOR. |
| 57 | VREF | I | RGMII input voltage reference. Must be set to VDDOR/2 when used as 1.8V HSTL, 2.5V SSTL_2, and 3.3V. Set to VDDOR when used as 2.5V LV CMOS. |
| 58 | TXD[0] | I | RGMII Transmit Data |
| 59 | TXD[1] | I | RGMII Transmit Data |
| 60 | TCX_CLK | I | RGMII Transmit Clock provides a 125 MHz, 25 MHz, or 2.5 MHz reference clock with ± 50 ppm tolerance depending on speed. |
| 61 | TXD[2] | I | RGMII Transmit Data |
| 62 | TXD[3] | I | RGMII Transmit Data |
| 63 | TX_CTRL | I | RGMII Transmit Control. TX_EN is presented on the rising edge of TX_CLK. A logical derivative of TX_EN and TX_ER is presented on the falling edge of TX_CLK. |
| 64 | CONFIG[0] | I | Hardware Configuration |
| EPAD | VSS | GND | Ground to device. The 64-pin QFN package has an exposed die pad (E-PAD) at its base. This E-PAD must be soldered to VSS. |
Jumbo frames
From Linux perspective (under OtherOS <=3.15), the old drivers set the MTU to 2308, while newer versions set the MTU of 1518. This could be a hypervisor restriction (needs research).
MTU is set with vsh using syscall net_ioctl (libnet)